Imagine standing in the middle of an endless desert, the sun hangs heavy as its golden rays dance on the rugged rocks scattered across the landscape. Beneath your feet, the sand is warm as you kneel to examine mysterious markings carved in the rocks. These ancient symbols, though weathered by time, seem to pulse with untold stories from a time when language was taking its first steps into the world. You can almost hear the faint echoes of tools chiseling into stone, the murmur of voices long silenced, and the rustling of a desert breeze that has carried these stories for centuries. Welcome to Saudi Arabia, a land where the past lives in stone, and the ancient scripts engraved across its landscapes wait patiently to reveal their timeless secrets.
The ancient scripts of Saudi Arabia are not merely historical relics but echoes of the earliest forms of written communication on the Arabian Peninsula. Each inscription offers a glimpse into a time when language was beginning to take form.
The Thamudic Script’s Secrets in the Sand

In the rugged landscapes of northwestern Saudi Arabia, the Thamudic people left their mark on rocks and cliffs. These ancient carvings, dating back to the 1st millennium BCE, hold the stories of their survival, faith, and life. One can easily imagine how their steady hands must have carved these symbols onto stones under the burning sun. These inscriptions served as a way of communication in an otherwise silent world, representing the first attempts by people in the region to communicate through written symbols. This script laid the foundation for future developments in the Arabic script, acting as a stepping stone to more complex forms of written language.
Imagine people of this era steadily striking a rocky surface with a chisel to carve a message, but what could these markings even mean? Some may claim that these are prayers seeking favor from gods unseen. Or perhaps documentation of trade and agreements that would spread across distant lands. Perhaps the carver was feeling poetic and wanted to draw words from the depths of their soul. Or maybe they are a mix of all of these.
The South Arabian Musnad Script of the Lost Kingdoms

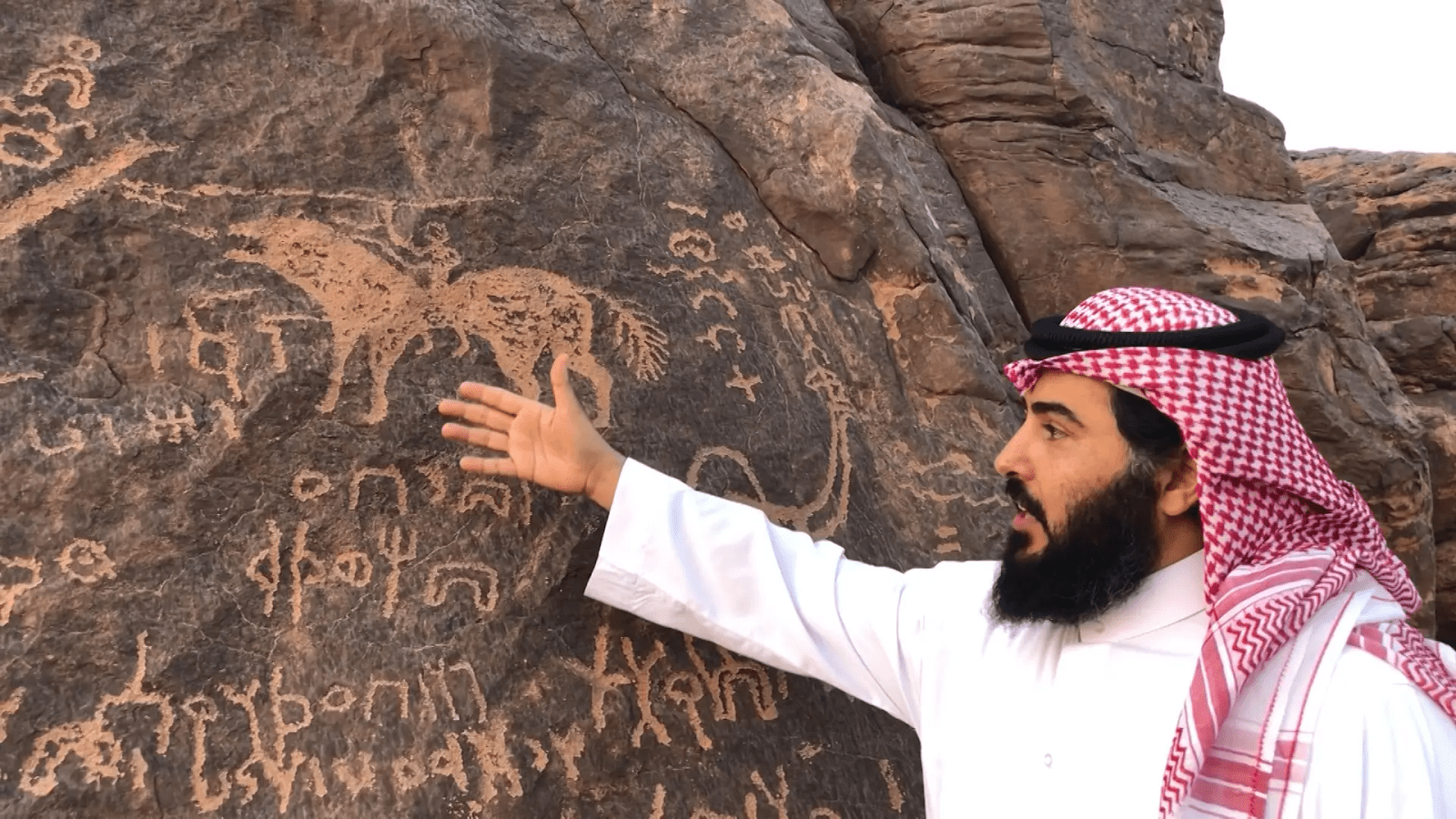
In the southern lands of Saudi Arabia, long before modern maps and borders, an ancient script called Musnad thrived. Between the 9th century BCE and the 6th century CE, this script became the voice of mighty kingdoms like Saba, Himyar, and Qataban. The language of these realms wasn’t just spoken, but carved into stone monuments that towered over ancient cities, pressed onto coins that passed through countless hands, and inscribed onto sacred walls that bore witness to countless prayers.
The South Arabian script is known for its clean, angular characters with a distinct and timeless look. They whispered of triumphs on ancient battlefields, echoed the clinking of trade deals sealed in distant markets, and stood as witnesses to the major events that shaped history.
The Nabataean Script, A Bridge Between Worlds
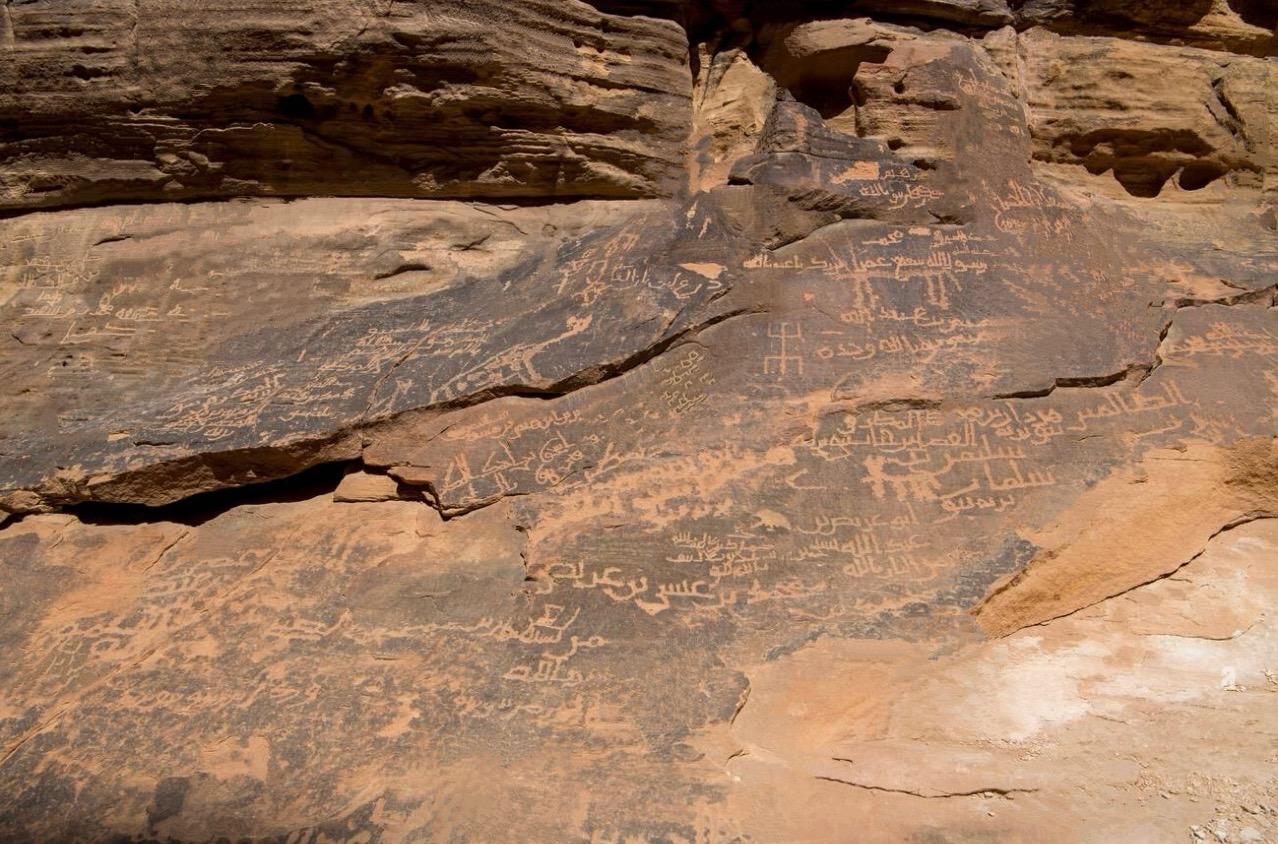

As we move further north, we encounter the Nabataean script, which emerged around the 4th century BCE. The Nabataeans, famed for the majestic city of Petra, were more than just builders; they were storytellers and dreamers. Their script, born from ancient traditions, carried the weight of their royal proclamations, personal thoughts, and the rhythm of their days. These inscriptions remain scattered across the landscapes of Saudi Arabia. In their quiet elegance, they continue to whisper tales of a vibrant world that once thrived.
The Nabataean script is important because it’s considered the direct precursor to the Arabic script. Over time, the Nabataeans began to simplify their writing. They made the style more fluid and cursive, characteristics that would come to define the Arabic script. The transition from Nabataean to Arabic was gradual, almost like a slow dance between tradition and innovation. The inscriptions left behind by the Nabataeans in places like Madain Saleh are some of the clearest examples of this transition. They’re a bridge between ancient writings and the flourishing Arabic language.
The Evolution of Arabic Script From Inscriptions to Art

By the time the Islamic Caliphate rose in the 7th century CE, the Arabic script had evolved into a system, not just as a means of communication, but an art form. Its flowing curves and elegant lines breathed life into Islamic culture, gracing everything from sacred manuscripts to grand architectural marvels, turning written words into timeless works of beauty.
However, the roots of Arabic calligraphy can be traced back to the ancient scripts of Saudi Arabia. The early inscriptions, Thamudic, Musnad, or Nabataean, laid the groundwork for the stunning beauty of Arabic script. What began as simple marks on stone eventually transformed into the art of calligraphy, with scholars and artists perfecting the craft over centuries.
Arabic calligraphy is more than just about writing but about beauty, harmony, and expression. Every curve, every stroke, is imbued with intention, telling stories of faith, culture, and creativity. Even today, the art of calligraphy thrives, its graceful lines a tribute to the enduring legacy of Saudi Arabia’s ancient scripts.
Uncovering the Ancient Scripts of Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia is far more than its sweeping deserts and oil-rich lands but a treasure trove of history. Whether you’re looking at the rock carvings of Al-‘Ula, exploring the inscriptions at Madain Saleh, or admiring the graceful lines of ancient Arabic calligraphy, the ancient scripts of this land open a portal to a world shaped by stories of the past. Each of these inscriptions, whether simple or elaborate, is a piece of the puzzle that tells the story of Saudi Arabia’s linguistic heritage. The inscriptions speak of kingdoms long gone, of people who once lived and loved, fought and prayed, and left their mark on the world.
The ancient scripts of Saudi Arabia are a bridge between the past and the present. They offer us a glimpse into a world that existed long before the rise of modern nations. A world where language was the key to understanding who we were, where we came from, and where we were going.
So, next time you find yourself standing in the desert, look down at the stones beneath your feet. You might just find a story waiting to be told.
FAQs
What are the main ancient scripts in Saudi Arabia?
Saudi Arabia is home to some of the most fascinating ancient scripts like Thamudic, South Arabian Musnad, and Nabataean. These scripts were used by early civilizations to record their daily lives, communicate, and leave behind stories that still speak to us today.
Where can I see these ancient inscriptions?
You can find these amazing inscriptions in places like Hegra (Madain Saleh) in AlUla, the rock art in Najran’s Bir Hima, and the petroglyphs in the Hail Region. Each location is a treasure chest of history and a must-visit for anyone interested in ancient culture.
Can I visit these sites on guided tours?
Absolutely! Guided tours are a great way to explore these sites. The guides bring the history to life with fascinating stories and details that you might miss on your own. They also make sure you understand the significance of what you’re seeing.